VCNet package
The VCNet module provides mainly for classes to implement a VCNet counterfactual generator.
DataCatalog: Implementation of a structure to manage tabular data on top of a pandas dataframe. The role of this class is mainly to set up the characteristics of the dataset for the classification and explanation tasks (specify which attribute is the target attribute, which are immutables, etc.) It also embed the pre-/post-processings of VCNet which allows, for instance, to get counterfactuals directly as pandas datastructures (see Examples)VCNet: It implements the core model of VCNet counterfactual generation. The core VCNet model is a neural architecture made of two parts: a classifier (a.k.a. predictor) and a counterfactual generator. The model has to be fitted on a training dataset. During the training, the two parts are fitted jointly. This is implemented as a lightning module which can be embed in a machine learning pipeline.PHVCNet: It implements a post-hoc version of VCNet. This means that the classifier has already been fitted in this case. The training of such model fits only the counterfactual generator part of the model.SKLearnClassifier: It is used with a post-hoc VCNet model when the classifier is a shallow model (not a deep model). This enable to embed a sklearn classifier or a XGBoost classifier to explain with counterfactuals.
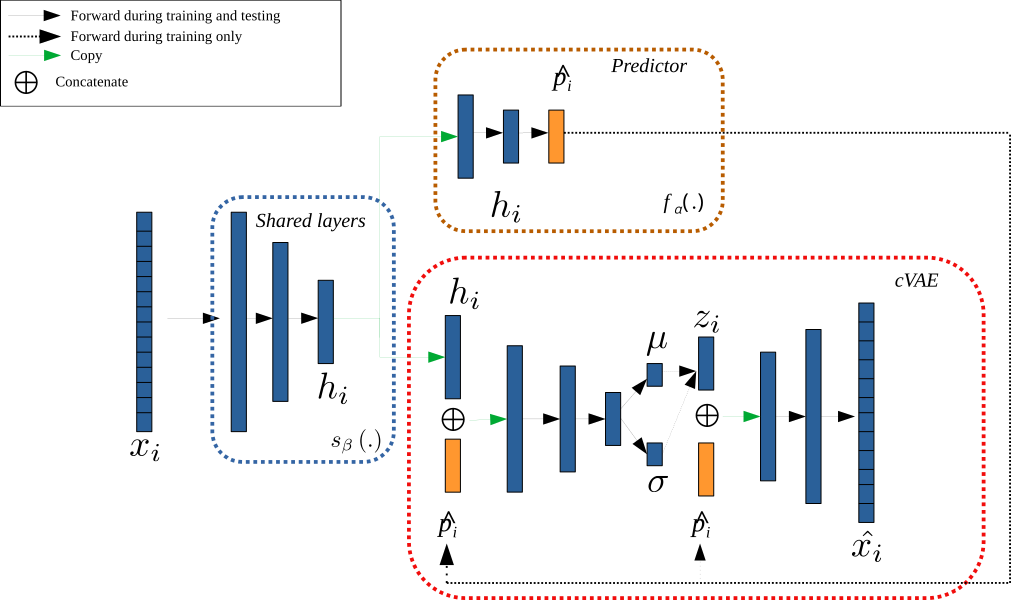
Illustration of the VCNet architecture
Submodules
vcnet.classifiers module
Classifier Models for VCNet.
A VCNet architecture is made of a counterfactual generator and a classifier. This module implements the classes for defining classifiers in the architecture.
Two classes are provided:
Classifier: the implementation of a default classifier architecture for the joint-model of VCNet. It is implemented as lighting module. The same architecture can be ued in a post-hoc model.SKLearnClassifier: the embedding of a shallow classifier to explain with post-hoc.
Note
You can define you own classifier by inheriting from one of these two classes.
Warning
SKLearnClassifier can not be used in a joint-learning fashion.
- class vcnet.classifiers.Classifier(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any)
Bases:
LightningModuleSimple fully convolutional classifier that is used bu default for the classification of numerical tabular data.
The network architecture is made of 3 fully connected layers, with relu activation function between layers and a sigmoid at the end.
The size of the layers are defined in the hyperparameters provided while the model is instanciated.
The mandatory parameters to define in the dictionary are:
the input size (in dataset>`feature_sze`)
the layer sizes (in the classifier_params : l1_size, l2_size and l3_size
the output size (in dataset>`class_sze`)
The learning rate (defined by lr in the classifier_params) is also recommanded. It’s default value is 0.01.
- Args:
hp (Dict): configuration of the classifier (hyperparameters) and the dataset.
- Raise:
KeyError is the settings does not contain all required parameter
- configure_optimizers()
- forward(x: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
Apply the classification model on the input x.
- Args:
x (torch.tensor): tensor of example to classify.
- Returns:
torch.tensor: the probabilistic classification vector
- class vcnet.classifiers.SKLearnClassifier(hp)
Bases:
objectWrapper for using a sklearn classifiers in the VCNet pipeline.
- Args:
hp (Dict): configuration of the classifier (hyperparameters) and the dataset
Example of minimal configuration:
Exemple of minimal dictionary to set up a
SKLearnClassifierin VCNet.hp = { "dataset": { "target":"income", }, "classifier_params" : { "skname": "RandomForestClassifier", "kwargs": { "n_estimators" : 50, } } } classifier = SKLearnClassifier(hp) classifier.fit(dataset.df_train)
Note
This class allows to use an XGBoostClassifier as classifier.
Note
We refer the user to the sklearn API to check the list of the classifier parameters. In case of use of XGBoost, parameters can be checked in the (XGBoost API)[https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/stable/python/sklearn_estimator.html]
- fit(X: pandas.DataFrame)
function to fit the model
- Args:
X (pd.DataFrame): dataset to train the model on
vcnet.data module
VCNet data module. This module provides the classes to manage the data for VCNet
- class vcnet.data.DataCatalog(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any)
Bases:
LightningDataModuleGeneric framework for datasets, using sklearn processing. This class is implemented by OnlineCatalog and CsvCatalog. OnlineCatalog allows the user to easily load online datasets, while CsvCatalog allows easy use of local datasets.
The preprocessing pipeline is made of the following steps: encoding of categorical attributes, data imputation and scaling. The reverse pipeline can also apply a rounding of numerical attributes.
- Args:
- config: Dict
Configuration dictionary containing the required and optional settings to prepare the dataset for counterfactual generation. The settings are used to setup an internal pipeline (and its reverse pipeline).
The settings must at least define the following attributes:
target (str) Name of the target attribute
continuous (List[str]): List of continuous attributes of the dataset
categorical (List[str]): List of categorical attributes of the dataset
immutables (List[str]): List of immutable attributes (among the continuous or categorical attributes)
If the dataset is store in a file, it can be loaded in the pipeline by setting the filename attribute
The following optional settings define the train/test sets:
test_size/val_size (float): proportions of the dataset dedicated to test and validation
stratify (bool): Use a stratification strategy to sample the test/train sets
The following optional settings define the pre-processing pipeline:
scaling_method (str, default: “MinMax”): Type of used sklearn scaler. Can be set with the property setter to any sklearn scaler. Set to “Identity” for no scaling.
encoding_method (str, default: “OneHot_drop_binary”) Type of OneHotEncoding (“OneHot” or “OneHot_drop_binary”). Additional drop binary decides if one column is dropped for binary features. Can be set with the property setter to any sklearn encoder. Set to “Identity” for no encoding.
imputation_method (str, default: “Identity”) Type of sklearn imputer (“SimpleImputer” or “Identity”). Set to “Identity” for no imputation.
activate_rounding (bool, default: False) If True, the continuous attributes values of a generated counterfactual will be rounded to be more realistic.
Finally, some other optional parameters: * batch_size (int): default value is 64
- Attributes:
- data_name: str
What name the dataset should have.
- df: pandas.DataFrame
The complete Dataframe. This is equivalent to the combination of df_train and df_test, although not shuffled.
- df_train: pandas.DataFrame
Training portion of the complete Dataframe.
- df_test: pandas.DataFrame
Testing portion of the complete Dataframe.
- df_val: pandas.DataFrame
Validation portion of the complete Dataframe.
Warning
Imputation works only for continuous variables.
Warning
The verification of the name of the attributes / target is not made at this stage, but when the dataset is prepared.
Warning
Rounding is applied to all numerical attributes or none. You can not choose the attribute on which the rounding will be applied. Nonetheless, the rounding setting (number of decimal) is automatically infered from the training data per attribute (two different attributes).
- class_encoding(y)
Compute the internal encoding of the class for given class labels.
- Args:
y: vector with class labels
- Returns:
The probabilistic representation of the class (one-hot encoding)
- data_unloader(X: torch.tensor, y: torch.tensor | numpy.array) pandas.DataFrame
Recreates a dataframe from the numerical tensors of data and labels internally used by VCNet models.
It applies the inverse transformation on data structured required internally by VCNet. Depending on the dataset parameters, it reverses the one-hot encoding to recreate readable categorical features for the user; it reverse the scaling of numerical attributes it could also apply rounding on numerical features; finally, it also recodes the class labels from probabilistic forecasts.
- Returns:
DataFrame: Dataframe with the same columns as input dataframe
Warning
In case the pre-processing included missing values imputations, this step is not reversed and the output dataset contains the imputed values.
- property df_test: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing prepared test data
- property df_train: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing prepared train data
- property df_val: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing prepared validation data
- property encoder: sklearn.base.BaseEstimator
Contains a fitted sklearn encoder:
Returns
sklearn.preprocessing.BaseEstimator
- get_pipeline_element(key: str) Callable
Returns a specific element of the transformation pipeline.
Parameters
- keystr
Element of the pipeline we want to return
Returns
Pipeline element
- property imputer: sklearn.base.BaseEstimator
Contains a fitted sklearn imputer:
Returns
sklearn.preprocessing.BaseEstimator
- inverse_transform(df: pandas.DataFrame) pandas.DataFrame
Transforms output after prediction back into original form. Only possible for DataFrames with preprocessing steps.
Parameters
- dfpd.DataFrame
Contains normalized and encoded data.
Returns
- outputpd.DataFrame
Prediction output denormalized and decoded
- prepare_data(raw_pd: pandas.DataFrame | None = None)
Data preparation
- Args:
- raw_pd (pd.DataFrame, optional): A pandas dataframe containing data to prepare.
Defaults to None.
- Returns: Dict or None
Updated settings ready for use in a VCNet model. If None, this means the data preparation failed.
- property raw_df_test: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing raw test data
- property raw_df_train: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing raw train data
- property raw_df_val: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing raw validation data
- property scaler: sklearn.base.BaseEstimator
Contains a fitted sklearn scaler.
Returns
sklearn.preprocessing.BaseEstimator
- property settings
Settings of the dataset
- test_dataloader() torch.utils.data.DataLoader
- train_dataloader() torch.utils.data.DataLoader
- transform(df: pandas.DataFrame) pandas.DataFrame
Transforms input for prediction into correct form. Only possible for DataFrames without preprocessing steps.
Recommended to keep correct encodings and normalization
Parameters
- dfpd.DataFrame
Contains raw (not normalized and not encoded) data.
Returns
- outputpd.DataFrame
Prediction input normalized and encoded
- val_dataloader() torch.utils.data.DataLoader
- class vcnet.data.NumpyDataset(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any)
Bases:
TensorDatasetDataset with only numerical attributes.
A numpy dataset is represented by a tensor with attributes in columns. When it is a training dataset, the last column is the numerical target feature.
- data_loader(batch_size=128, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
Builder of a torch data loader to be use for training VCNet
- Args:
batch_size (int, optional): Size of the Batch. Defaults to 128. shuffle (bool, optional): Shuffle or not the examples before creating batches.
Defaults to True.
num_workers (int, optional): Number of threads. Defaults to 4.
- Returns:
torch.DataLoader: representation of a dataset for mini-batch optimization
- features(test=False)
Returns the feature part of the tensor
- Args:
- test (bool, optional): indicates whether the dataset contains labels (False)
or not (True). Defaults to False.
- target(test=False)
Returns the labels of the dataset (if exists, otherwise it returns None)
- Args:
test (bool, optional): indicates whether the dataset contains labels (False) or not (True). Defaults to False.
- class vcnet.data.PostHocRounder(precisions)
Bases:
objectA class dedicated to rounding values at a given decimal. This is a post-hoc rounder as it applied a rounding on the numerical values generated by VCNet to provide more realistic values.
The class implement an inverse_transform only, as it apply the transformation on generate counterfactuals.
- Args:
precisions (Dict(str,int)): map that gives the precision to apply to an attribute name
- inverse_transform(df)
Apply the inverse transformation on the dataframe df.
- vcnet.data.attribute_round(fitted_rounder: PostHocRounder, features: List[str], df: pandas.DataFrame) pandas.DataFrame
Pipeline function to round data the numeraical attributes.
Parameters
- fitted_rounderRounder
Round the attribute of the data at a fitter level of precision
- featureslist
List of continuous feature
- dfpd.DataFrame
Data we want to round
Returns
- outputpd.DataFrame
Whole DataFrame with rounded values
- vcnet.data.decode(fitted_encoder: sklearn.base.BaseEstimator, features: List[str], df: pandas.DataFrame) pandas.DataFrame
Pipeline function to decode data with fitted sklearn OneHotEncoder.
Parameters
- fitted_encodersklearn OneHotEncoder
Encodes input data.
- featureslist
List of categorical feature.
- dfpd.DataFrame
Data we want to normalize
Returns
- outputpd.DataFrame
Whole DataFrame with encoded values
- vcnet.data.descale(fitted_scaler: sklearn.base.BaseEstimator, features: List[str], df: pandas.DataFrame) pandas.DataFrame
Pipeline function to de-normalize data with fitted sklearn scaler.
Parameters
- fitted_scalersklearn Scaler
Normalizes input data
- featureslist
List of continuous feature
- dfpd.DataFrame
Data we want to de-normalize
Returns
- outputpd.DataFrame
Whole DataFrame with de-normalized values
- vcnet.data.encode(fitted_encoder: sklearn.base.BaseEstimator, features: List[str], df: pandas.DataFrame) pandas.DataFrame
Pipeline function to encode data with fitted sklearn OneHotEncoder.
Parameters
- fitted_encodersklearn OneHotEncoder
Encodes input data.
- featureslist
List of categorical feature.
- dfpd.DataFrame
Data we want to normalize
Returns
- outputpd.DataFrame
Whole DataFrame with encoded values
- vcnet.data.fit_encoder(encoding_method, df)
Parameters
- encoding_method: {“OneHot”, “OneHot_drop_binary”, “Identity”}
String indicating what encoding method to use or sklearn.preprocessing function.
- df: pd.DataFrame
DataFrame containing only categorical data.
Returns
sklearn.base.BaseEstimator
- vcnet.data.fit_imputer(imputation_method, df)
Parameters
- imputation_method: {“SimpleImputer”,”Identity”}
String indicating what scaling method to use or sklearn.impute function.
- df: pd.DataFrame
DataFrame only containing continuous data.
Returns
sklearn.base.BaseEstimator
- vcnet.data.fit_rounder(df)
Function that build a rounder from a dataframe.
Parameters
- df: pd.DataFrame
DataFrame only containing continuous data.
Returns
Rounder
- vcnet.data.fit_scaler(scaling_method, df)
Parameters
- scaling_method: {“MinMax”, “Standard”, “Identity”}
String indicating what scaling method to use or sklearn.preprocessing function.
- df: pd.DataFrame
DataFrame only containing continuous data.
Returns
sklearn.base.BaseEstimator
- vcnet.data.impute(fitted_imputer: sklearn.base.BaseEstimator, features: List[str], df: pandas.DataFrame) pandas.DataFrame
Pipeline function to impute missing values in the dataset with a fitted sklearn Imputer. This function has to be applied once the
Parameters
- fitted_imputersklearn Imputer
Imputes missing values.
- featureslist
List of numerical feature.
- dfpd.DataFrame
Data we want to modify
Returns
- outputpd.DataFrame
Whole DataFrame without missing values (in the selected features)
- vcnet.data.order_data(feature_order: List[str], df: pandas.DataFrame) pandas.DataFrame
Restores the correct input feature order for the ML model
Only works for encoded data
Parameters
- feature_orderlist
List of input feature in correct order
- dfpd.DataFrame
Data we want to order
Returns
- outputpd.DataFrame
Whole DataFrame with ordered feature
- vcnet.data.scale(fitted_scaler: sklearn.base.BaseEstimator, features: List[str], df: pandas.DataFrame) pandas.DataFrame
Pipeline function to normalize data with fitted sklearn scaler.
Parameters
- fitted_scalersklearn Scaler
Normalizes input data
- featureslist
List of continuous feature
- dfpd.DataFrame
Data we want to normalize
Returns
- outputpd.DataFrame
Whole DataFrame with normalized values
vcnet.models module
Module for the VCNet models
- class vcnet.models.PHVCNet(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any)
Bases:
VCNetBaseClass for Post-hoc VCNet immutable version model architecture. Post-hoc VCNet uses a torch classifier trained on a classification task and trains the counterfactual generators.
A classifier provided to this class is assumed to take examples to be classified.
- classif(z: torch.tensor, x: torch.tensor, x_mut: torch.tensor, x_immut: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
Forward function of the classification layers. It predicts the class of an example z prepared by the encode_classif function.
- Args:
z (torch.tensor): examples represented in their latent space for classification.
- Returns:
torch.tensor: example classification. Dimension of the output: self.class_size.
- training_step(batch, batch_idx)
Training step for lightning
- Args:
batch (torch.tensor): batch batch_idx (torch.tensor): list of example indices
- Returns:
float: loss measure for the batch
- class vcnet.models.VCNet(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any)
Bases:
VCNetBaseClass for VCNet immutable version model architecture. VCNet is a joint learning architecture: during the training phase, both the classifier and the counterfactual generators are fitted.
- classif(z: torch.tensor, x: torch.tensor, x_mut: torch.tensor, x_immut: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
Forward function of the classification layers. It predicts the class of an example z prepared by the encode_classif function.
- Args:
z (torch.tensor): examples represented in their latent space for classification.
- Returns:
torch.tensor: example classification. Dimension of the output: self.class_size.
- loss_functions(recon_x, x, mu, sigma, output_class=None, y_true=None)
Evaluation of the VCNet losses
- pre_encode(x_mut: torch.tensor, x_immut: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
Function that prepares examples (x) with a shared pre-coding layers.
The default behavior is to transmit x as it.
- training_step(batch, batch_idx)
Training step for lightning
- Args:
batch (torch.tensor): batch batch_idx (torch.tensor): list of example indices
- Returns:
float: loss measure for the batch
- class vcnet.models.VCNetBase(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any)
Bases:
LightningModule,ABCClass for the general VCNet architecture with handling immutable features. This class is abstract. It specifies a VCNet model with a classifier and a conditional variational auto-encoder (cVAE) and a training procedure. The training procedure of a VCNet architecture consists in training the cVAE in a classical way. The VCNet trick lies in generating counterfactuals by switching the predicted class of an example to generate a modified example using the cVAE.
The VCNet architecture handles natively the immutable features.
Note
Note that this VCNet architecture handles only numerical features. The user of this class has to manage the encoding of categorical features out of this class.
VCNet has also a strategy for counterfactual class choice, in case of a more-than-two-class classification problem. The way the probability vector depends on two parameters to set up in the hyper parameters:
class_change (reverse by default or second_max): define the strategy to find the most appropriate alternative class.
̀ class_change_norm` (“sum-norm” by default, “softmax” or “absolute”): define how the changed probability vector is normalized.
Example
Let assume the class probabilities vector is \([0.3, 0.6, 0.1]\). In the reverse strategy, the resulting vector will by \([0.7, 0.4, 0.9]\): it favors the class with the lower predicted probability to be chosen to generate counterfactuals. In the second_max strategy, it yields the vector \([0.3, 0.0, 0.1]\) … and then, it is the secondly predicted class that is used to generate counterfactuals.
In practice, these vectors are not used as it, but are normalized … and there are three different ways to normalize them: “sum-norm” will normalized using the sum of vector elements in the first strategy, we obtain the final vector \([0.35, 0.2, 0.45]\); “softmax” applies the
softmax()function to make a similar normalisation; while “absolute” will yields the vector \([0.0, 0.0, 1.0]\) to force the counterfactual to be purely an example like the third class.- abstract classif(z: torch.tensor, x: torch.tensor, x_mut: torch.tensor, x_immut: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
Forward function of the classification layers. It predicts the class of an example z prepared by the encode_classif function.
- Args:
z (torch.tensor): examples represented in their latent space for classification.
- Returns:
torch.tensor: example classification. Dimension of the output: self.class_size.
- configure_optimizers()
Setup of the optimizer
- counterfactuals(x: torch.tensor, t: torch.tensor = None) torch.tensor
Generation of counterfactuals for the example x.
- Args:
x (torch.tensor): a single factual for which a counterfactual is generated t (torch.tensor): a targeted class (probabilistic vector)
- decode(z_prime: torch.tensor, c: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
C-VAE decoding, computes \(P(x|z, c)\)
- Args:
z_prime (torch.tensor): vector to encode c (torch.tensor): conditioning of the VAE.
For VCNet, the decoding is conditioned by the class and the immutable features \([class, x_immutable]\). Then, its dimension is \(class_size + len(x_immutable)\)
- Returns:
torch.tensor: decoded instances out of the cVAE
- encode(z: torch.tensor, x_mut: torch.tensor, x_immut: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
C-VAE encoding
- Args:
z (torch.tensor): pre-encoded input representation.
None or tensor of size defined by latent_size_share
x_mut (torch.tensor): mutable part of the input tensor x_immut (torch.tensor): mutable part of the input tensor
- Returns:
tuple (torch.tensor, torch.tensor):
Representation of the gaussian distribution in the latent space (mu, sigma). Tensors of dimension latent_size.
- forward(x: torch.tensor)
Forward function used during the training phase of a VCNet model. It mainly goes through the three parts of the models: the pre-coding, the C-VAE and the classification. Finally, it returns the reconstructed example, the output class and VAE distribution parameters.
- Args:
x (torch.tensor): input examples
- forward_pred(x: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
Forward function for prediction in test phase (prediction task). It prepares the examples and then classify it
- Args:
x (torch.tensor): an tensor containing examples
- loss_functions(recon_x, x, mu, sigma, output_class=None, y_true=None)
Evaluate the loss of the reconstruction
- pre_encode(x_mut: torch.tensor, x_immut: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
Function that prepares examples (x) with a shared pre-coding layers.
The default behavior is to transmit x as it.
- reparameterize(mu: torch.tensor, sigma: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
C-VAE Reparametrization trick
- Args:
mu (torch.tensor): size latent_size sigma (torch.tensor): size latent_size
- Returns:
torch.tensor: size latent_size
Module contents
VCNet Module
- class vcnet.DataCatalog(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any)
Bases:
LightningDataModuleGeneric framework for datasets, using sklearn processing. This class is implemented by OnlineCatalog and CsvCatalog. OnlineCatalog allows the user to easily load online datasets, while CsvCatalog allows easy use of local datasets.
The preprocessing pipeline is made of the following steps: encoding of categorical attributes, data imputation and scaling. The reverse pipeline can also apply a rounding of numerical attributes.
- Args:
- config: Dict
Configuration dictionary containing the required and optional settings to prepare the dataset for counterfactual generation. The settings are used to setup an internal pipeline (and its reverse pipeline).
The settings must at least define the following attributes:
target (str) Name of the target attribute
continuous (List[str]): List of continuous attributes of the dataset
categorical (List[str]): List of categorical attributes of the dataset
immutables (List[str]): List of immutable attributes (among the continuous or categorical attributes)
If the dataset is store in a file, it can be loaded in the pipeline by setting the filename attribute
The following optional settings define the train/test sets:
test_size/val_size (float): proportions of the dataset dedicated to test and validation
stratify (bool): Use a stratification strategy to sample the test/train sets
The following optional settings define the pre-processing pipeline:
scaling_method (str, default: “MinMax”): Type of used sklearn scaler. Can be set with the property setter to any sklearn scaler. Set to “Identity” for no scaling.
encoding_method (str, default: “OneHot_drop_binary”) Type of OneHotEncoding (“OneHot” or “OneHot_drop_binary”). Additional drop binary decides if one column is dropped for binary features. Can be set with the property setter to any sklearn encoder. Set to “Identity” for no encoding.
imputation_method (str, default: “Identity”) Type of sklearn imputer (“SimpleImputer” or “Identity”). Set to “Identity” for no imputation.
activate_rounding (bool, default: False) If True, the continuous attributes values of a generated counterfactual will be rounded to be more realistic.
Finally, some other optional parameters: * batch_size (int): default value is 64
- Attributes:
- data_name: str
What name the dataset should have.
- df: pandas.DataFrame
The complete Dataframe. This is equivalent to the combination of df_train and df_test, although not shuffled.
- df_train: pandas.DataFrame
Training portion of the complete Dataframe.
- df_test: pandas.DataFrame
Testing portion of the complete Dataframe.
- df_val: pandas.DataFrame
Validation portion of the complete Dataframe.
Warning
Imputation works only for continuous variables.
Warning
The verification of the name of the attributes / target is not made at this stage, but when the dataset is prepared.
Warning
Rounding is applied to all numerical attributes or none. You can not choose the attribute on which the rounding will be applied. Nonetheless, the rounding setting (number of decimal) is automatically infered from the training data per attribute (two different attributes).
- class_encoding(y)
Compute the internal encoding of the class for given class labels.
- Args:
y: vector with class labels
- Returns:
The probabilistic representation of the class (one-hot encoding)
- data_unloader(X: torch.tensor, y: torch.tensor | numpy.array) pandas.DataFrame
Recreates a dataframe from the numerical tensors of data and labels internally used by VCNet models.
It applies the inverse transformation on data structured required internally by VCNet. Depending on the dataset parameters, it reverses the one-hot encoding to recreate readable categorical features for the user; it reverse the scaling of numerical attributes it could also apply rounding on numerical features; finally, it also recodes the class labels from probabilistic forecasts.
- Returns:
DataFrame: Dataframe with the same columns as input dataframe
Warning
In case the pre-processing included missing values imputations, this step is not reversed and the output dataset contains the imputed values.
- property df_test: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing prepared test data
- property df_train: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing prepared train data
- property df_val: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing prepared validation data
- property encoder: sklearn.base.BaseEstimator
Contains a fitted sklearn encoder:
Returns
sklearn.preprocessing.BaseEstimator
- get_pipeline_element(key: str) Callable
Returns a specific element of the transformation pipeline.
Parameters
- keystr
Element of the pipeline we want to return
Returns
Pipeline element
- property imputer: sklearn.base.BaseEstimator
Contains a fitted sklearn imputer:
Returns
sklearn.preprocessing.BaseEstimator
- inverse_transform(df: pandas.DataFrame) pandas.DataFrame
Transforms output after prediction back into original form. Only possible for DataFrames with preprocessing steps.
Parameters
- dfpd.DataFrame
Contains normalized and encoded data.
Returns
- outputpd.DataFrame
Prediction output denormalized and decoded
- prepare_data(raw_pd: pandas.DataFrame | None = None)
Data preparation
- Args:
- raw_pd (pd.DataFrame, optional): A pandas dataframe containing data to prepare.
Defaults to None.
- Returns: Dict or None
Updated settings ready for use in a VCNet model. If None, this means the data preparation failed.
- property raw_df_test: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing raw test data
- property raw_df_train: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing raw train data
- property raw_df_val: pandas.DataFrame
Dataframe containing raw validation data
- property scaler: sklearn.base.BaseEstimator
Contains a fitted sklearn scaler.
Returns
sklearn.preprocessing.BaseEstimator
- property settings
Settings of the dataset
- test_dataloader() torch.utils.data.DataLoader
- train_dataloader() torch.utils.data.DataLoader
- transform(df: pandas.DataFrame) pandas.DataFrame
Transforms input for prediction into correct form. Only possible for DataFrames without preprocessing steps.
Recommended to keep correct encodings and normalization
Parameters
- dfpd.DataFrame
Contains raw (not normalized and not encoded) data.
Returns
- outputpd.DataFrame
Prediction input normalized and encoded
- val_dataloader() torch.utils.data.DataLoader
- class vcnet.PHVCNet(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any)
Bases:
VCNetBaseClass for Post-hoc VCNet immutable version model architecture. Post-hoc VCNet uses a torch classifier trained on a classification task and trains the counterfactual generators.
A classifier provided to this class is assumed to take examples to be classified.
- classif(z: torch.tensor, x: torch.tensor, x_mut: torch.tensor, x_immut: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
Forward function of the classification layers. It predicts the class of an example z prepared by the encode_classif function.
- Args:
z (torch.tensor): examples represented in their latent space for classification.
- Returns:
torch.tensor: example classification. Dimension of the output: self.class_size.
- training_step(batch, batch_idx)
Training step for lightning
- Args:
batch (torch.tensor): batch batch_idx (torch.tensor): list of example indices
- Returns:
float: loss measure for the batch
- class vcnet.SKLearnClassifier(hp)
Bases:
objectWrapper for using a sklearn classifiers in the VCNet pipeline.
- Args:
hp (Dict): configuration of the classifier (hyperparameters) and the dataset
Example of minimal configuration:
Exemple of minimal dictionary to set up a
SKLearnClassifierin VCNet.hp = { "dataset": { "target":"income", }, "classifier_params" : { "skname": "RandomForestClassifier", "kwargs": { "n_estimators" : 50, } } } classifier = SKLearnClassifier(hp) classifier.fit(dataset.df_train)
Note
This class allows to use an XGBoostClassifier as classifier.
Note
We refer the user to the sklearn API to check the list of the classifier parameters. In case of use of XGBoost, parameters can be checked in the (XGBoost API)[https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/stable/python/sklearn_estimator.html]
- fit(X: pandas.DataFrame)
function to fit the model
- Args:
X (pd.DataFrame): dataset to train the model on
- class vcnet.VCNet(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any)
Bases:
VCNetBaseClass for VCNet immutable version model architecture. VCNet is a joint learning architecture: during the training phase, both the classifier and the counterfactual generators are fitted.
- classif(z: torch.tensor, x: torch.tensor, x_mut: torch.tensor, x_immut: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
Forward function of the classification layers. It predicts the class of an example z prepared by the encode_classif function.
- Args:
z (torch.tensor): examples represented in their latent space for classification.
- Returns:
torch.tensor: example classification. Dimension of the output: self.class_size.
- loss_functions(recon_x, x, mu, sigma, output_class=None, y_true=None)
Evaluation of the VCNet losses
- pre_encode(x_mut: torch.tensor, x_immut: torch.tensor) torch.tensor
Function that prepares examples (x) with a shared pre-coding layers.
The default behavior is to transmit x as it.
- training_step(batch, batch_idx)
Training step for lightning
- Args:
batch (torch.tensor): batch batch_idx (torch.tensor): list of example indices
- Returns:
float: loss measure for the batch